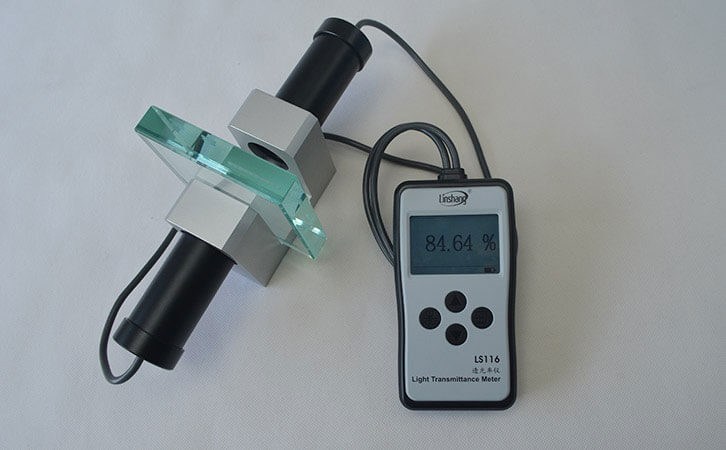
The Qualifications of High-precision Light Transmittance Tester
The light transmittance tester, also called the light transmittance meter, can be used to measure the visible light transmittance of various films, glass, acrylic, plastic and other materials. At present, most light transmittance testers have an accuracy of ±2%, but there are also higher precision light transmittance testers with an accuracy of ±1%. Such high-precision transmittance testers have higher hardware requirements.
So what are the qualifications for a high-precision transmittance tester?
1. Parallel light
We all know that when light enters another medium from one medium, it will refract at the interface and change the direction of light propagation. However, if a parallel beam of light is incident perpendicularly, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are both 0, and the direction of the refracted ray will coincide with the original direction. Therefore, compared with a light source designed by a point source, a light transmittance tester using a parallel light design reduces the transmittance error caused by the refraction of light. This advantage of parallel light is more pronounced when measuring large thickness materials.
2. In line with CIE photopic luminosity function
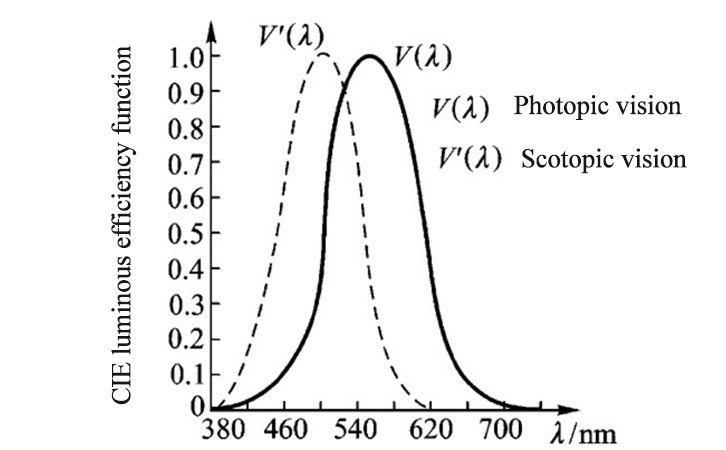
The International Commission on Illumination (CIE) determines the relative sensitivity of the human eye to various wavelengths of light, based on a large number of observations from many people, called spectral spectroscopy efficiency or visual function (as shown below). The high-precision light transmittance tester generally uses a light source that conforms to internationally accepted standards, which can reduce errors in measurement data and authoritative organization standard data, and improve accuracy. For example, the LS116 high-precision transmittance tester is a device that complies with the CIE photopic luminosity function.
3. The stability of the light source and the uniformity of the light spot
The high-precision light transmittance tester generally uses an high-quality light source and uses a constant current source to supply power to the light source, ensuring stable light-emitting efficiency and uniformity of the light spot after long-term use of the light source. In addition, the temperature compensation function of the instrument can make the data of the light transmittance tester not affected by the change of light intensity and improve the measurement accuracy.

4. Using high-resolution 24-bit ADC acquisition chip to achieve real-time dynamic calibration
The high-precision light transmittance tester should use a high-resolution 24-bit ADC acquisition chip. Such a chip can improve the overall performance of the sensor inside the instrument, speed up the operation to achieve fast response, dynamic calibration and high resolution. Therefore, such a light transmittance tester can still ensure the accuracy of data when it is measured multiple times.
The above four points are the qualifications of a high-precision transmittance tester. At present, Linshang Technology's LS116 light transmittance tester have all the above qualifications, and is also a high-precision light transmittance tester with high cost performance in the industry.
- Linshang Insulated Glass Unit Measuring Tools
- Spectacle lens anti-blue light detection---blue-violet light transmittance meter
- Measurement of Optical Density
- Difference of LS116 Transmission & LS117 OD Meter
- Difference between LS116 and LS117 Light Transmittance Meter
- What’s the Difference Between Point Light and Parallel Light Transmittance Meter
